Introduction
Interactive Process Mining (IPM) results from the application of Interactive Pattern Recognition methodologies to Process Mining technologies. As a result, IPM is a paradigm that involves health professionals in the middle of the understanding of the process, until an Interactive Process Indicator (IPI) is defined. The IPI can be computed from the data available in the system and through iterative data rodeos sessions.
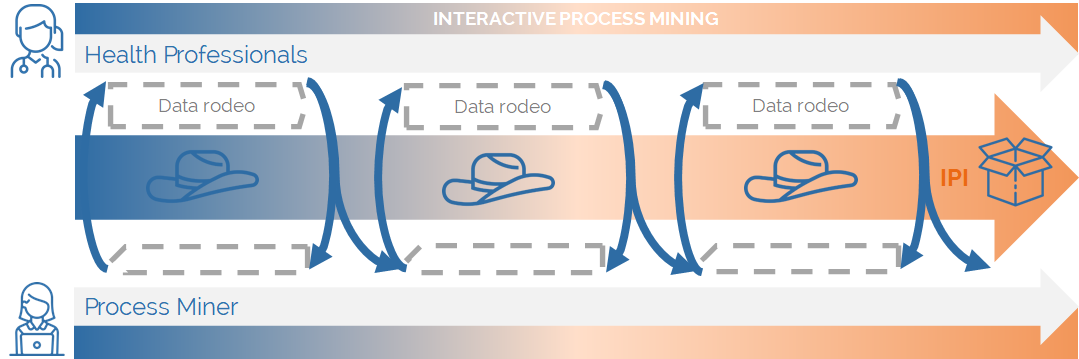 Figure 1. Interactive Process Mining
Figure 1. Interactive Process Mining
Through data rodeos, health professionals will be able to:
- iteratively define a process indicator according to the health organization needs with the help of the process miner
- analyze and validate the process indicator and
- be trained in the use of the process indicator.
Once an IPI is defined, the health professional is ready to analyse the data by means of PMApp tool.
Stakeholders
Process miner is an expert in IPM that guides and interacts with health professionals and the other stakeholders from the health centre during data rodeos until defining an IPI.
From the health organization the three main professionals involved in IPM are:
- Managers, because they have a wider view of the functioning of the health centre;
- Health professionals (HP), because they are the main holders of medical information, in terms of experience and knowledge and
- Information Technology (IT) professionals, because they have access to all data sources.
Interactive Process Indicator
An IPI is a way of understanding, measuring, and optimizing a process, letting the expert navigate through the model, discovering characteristics of the process, facilitating the analysis of individual and custom aspects that range from general to individual. An IPI is not just numbers, but also advanced views as enriched processes that bring an understandable view to the expert, helping to better perceive the processes for a deeper evaluation.
An IPI could be considered as a set of enriched Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), where:
-
The KPIs make assumptions of the process in order to perform the calculations. However, the IPIs work with the actual process.
-
KPIs need to be designed by a data analyst. On the other hand, IPIs are created by clinical staff (with the help of process miners during data rodeo sessions).
-
KPIs answer predefined questions, while IPIs allow you to ask as many questions as necessary.
-
KPIs give quantitative answers. Instead, IPIs in addition to giving quantitative answers, are visual and navigable models that let go from general to individual information.
IPM is divided into three phases where the definition of the IPI is done:
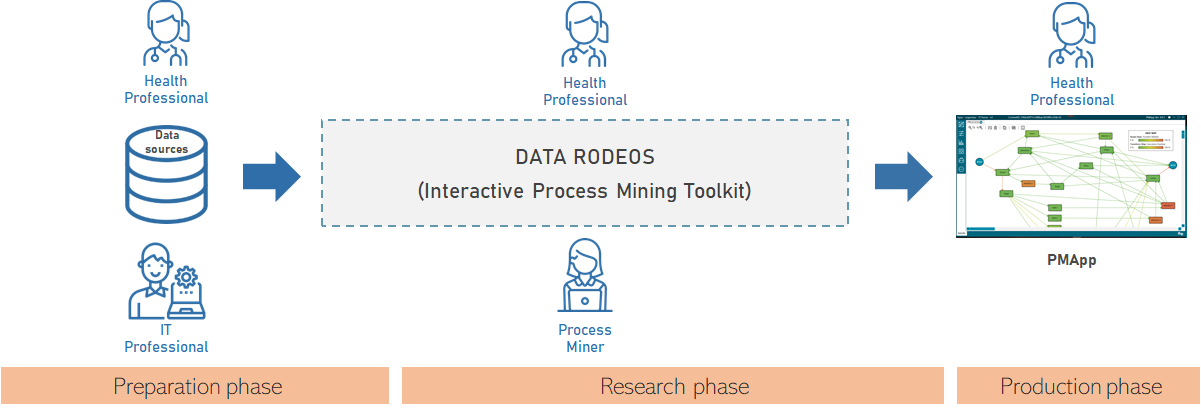 Figure 2. Interactive Process Mining process
Figure 2. Interactive Process Mining process
- Preparation phase. It comprises the first contact with the health organization, is explained the scope of the project and steps to follow and is provided access to the raw data to the process miner.
- Research phase. The process miner uses IPMT to generate an experiment configuration (runner) file based on health professionals requirements during datarodeos sessions, being PMApp tool tailored based on this configuration file.
- Production phase. Health professionals use PMApp in their daily practice.