Ingestor editor
The main aim of the ingestor is to manage data to deal with data quality and define events and metadata associated to the process.
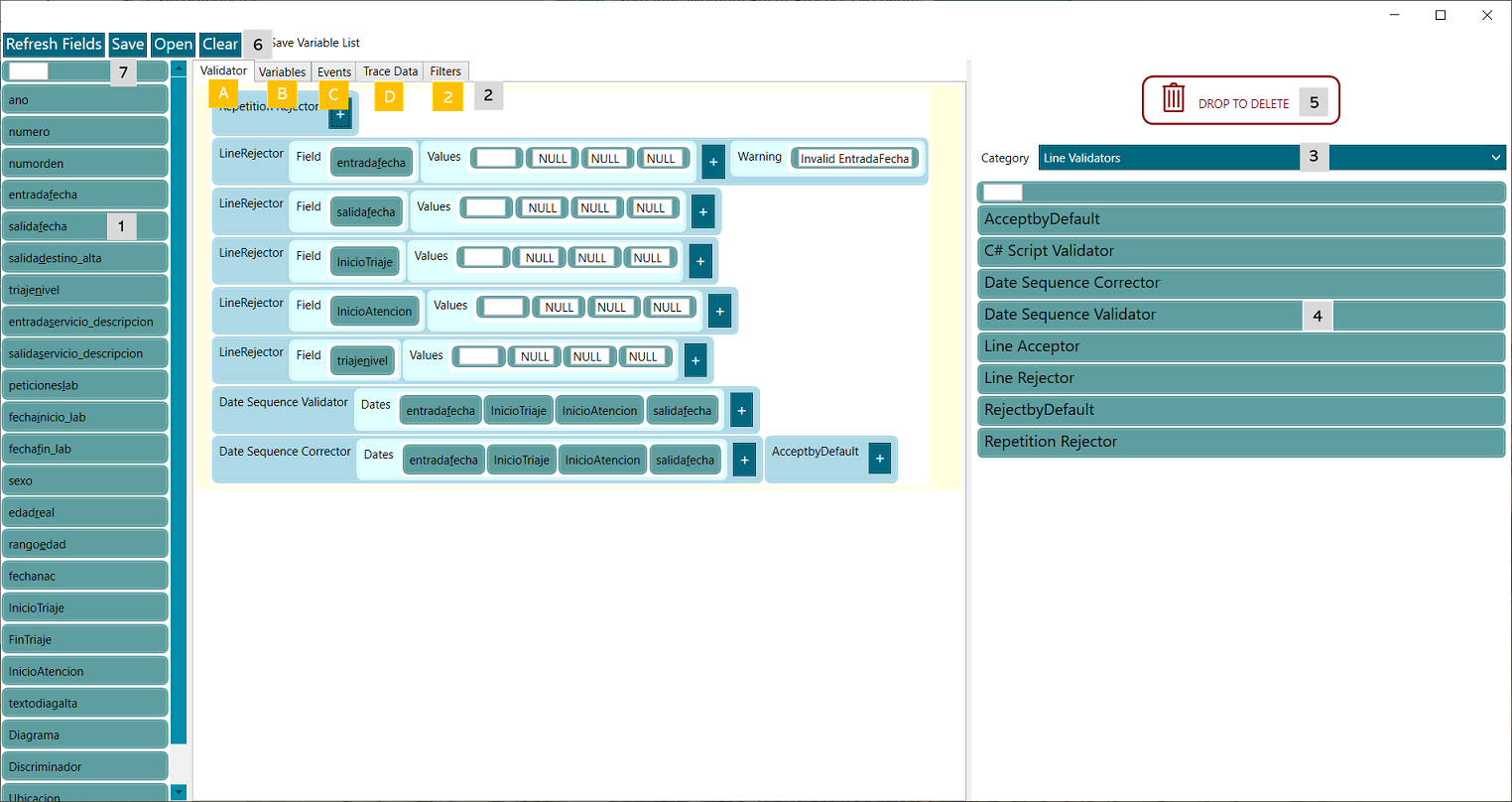 Figure 5. Ingestor editor
Figure 5. Ingestor editor
Factory area
(1). In the Factory area of the Experiment designer is indicated the data sources where the available fields (blocks) in this section, come from (e.g. headers from a CSV file).
-
By hovering the mouse on each field, you can see the initial 6 values.
-
The blocks are draggable to the corresponding tab.
-
There is an extra blank field (7) that adds extra capabilities to the Ingestor editor, since it enables the addition of new fields in specific blocks.
Ingestion area
(2). The ingestion is processed in the order that the tabs, (yellow steps) A to 2, are. This means e.g. that if a variable is generated (step A), it cannot be used by the validator (which has already been processed).
- (A) Validator tab. Category Line Validator of the section (3). The validators identify what raw data is valid or not.
- A Line Validator is intended to filter the rows that should be accepted or rejected by the ingestor.
- The Line Validators are processed in order sequentially.
- A Validator validates a specific field of a row.
- The extra blank field (7) can be used to add more values to validate the field, for example, entry_date must be different to NULL or blank.
- When any Validator determines that a row should be accepted or discarded the process stops, being that row never checked again, passing to the next row.
- Line Validators have a Warning parameter where a text can be added to indicate why the row was rejected. This warning will appear in the Ingestion report.
- If the Validator does not have a decision (it returns null) the ingestor passes to the next validator.
- Usually, the last validator block is an AcceptbyDefault or a RejectbyDefault validator block that accepts or rejects the row, respectively.
- (B) Variables tab. Category Variable Operations of the section (3). You may generate new variables that will turn into virtual fields (those fields do not exist in the log, but they may be used in the next tabs as if they existed there).
- New variables may be created by combining other variables, extracting information from a field, etc. For example, to calculate the age of the patient at the moment of the attention as in the following picture.
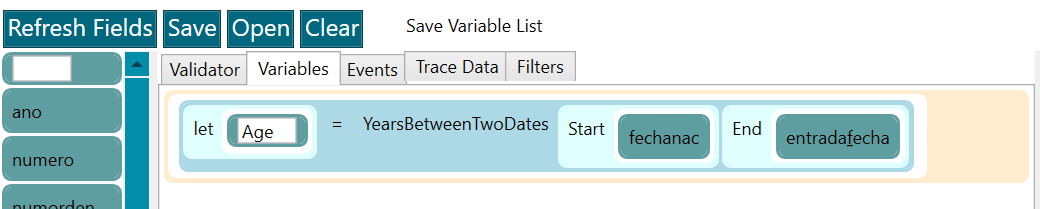 Figure 6. Ingestor editor - variables
Figure 6. Ingestor editor - variables
- New variables may be created by combining other variables, extracting information from a field, etc. For example, to calculate the age of the patient at the moment of the attention as in the following picture.
- (C) Events tab. Category Events of the section (3). Events are those that will be generated in the TPA.
- An event block allows the creation or extraction of one or more events based on the lines received from the Line Validators step.
- To define an event, it is needed an ID, activity name, start_timetamp, and end_timestamp, although this last one is not mandatory, depends on each case.
- Metadata can be associated to events by clicking in the + button of each one.
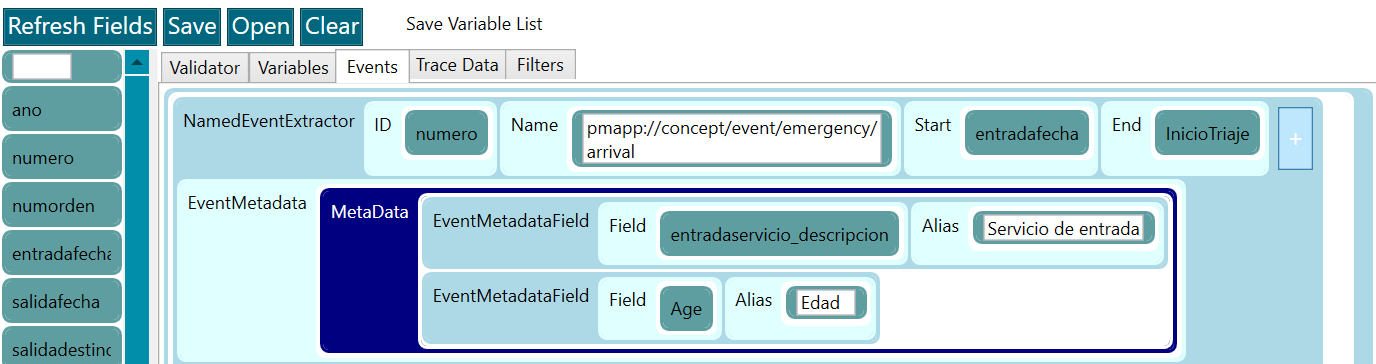 Figure 7. Ingestor editor - events
Figure 7. Ingestor editor - events
- (D) Trace Data tab. Category Trace data of the section (3). Trace data that are added as metadata to the trace is set up here.
- This enables to perform specific statistics afterwards.
- (2) Filters. Traces may be filtered by (none,) one or more blocks.
- These are the same filters as in the data rodeo process.
- Filters are applied to the Logs.
- Every ingestor generates one Log.
Blocks area
(3) Categories. The drop down contains five option, one per step of the ingestion process. Every option lists the blocks corresponding to a specific yellow step.
(4) Blocks. The blocks may be dragged and dropped into the corresponding tab.
(5) Delete. To delete a block just drag it and drop over the button DROP TO DELETE.
(6) Buttons. Buttons on top of the ingestor editor
-
Refresh Fields, to update the list of fields (1), for example, when a new variable has been created and it is needed to be used in the Events tab.
-
Save, it is needed to click on the Save button before closing the Ingestor editor, otherwise the changes will be lost.
-
Clear, it removes all the components in all the tabs.
(7) Additional field. It is an extra blank field that adds extra capabilities to the Ingestor editor, since it allows to add new fields in specific blocks.