Node Information perspective
The NODE INFORMATION perspective displays:
- Statistics about traces (like the ones shown in the tooltips)
- A histogram, which shows:
- The number of trace runs and the time taken for each
- The process view where the node selection was made (shown in figure 1, with the node highlighted in yellow)
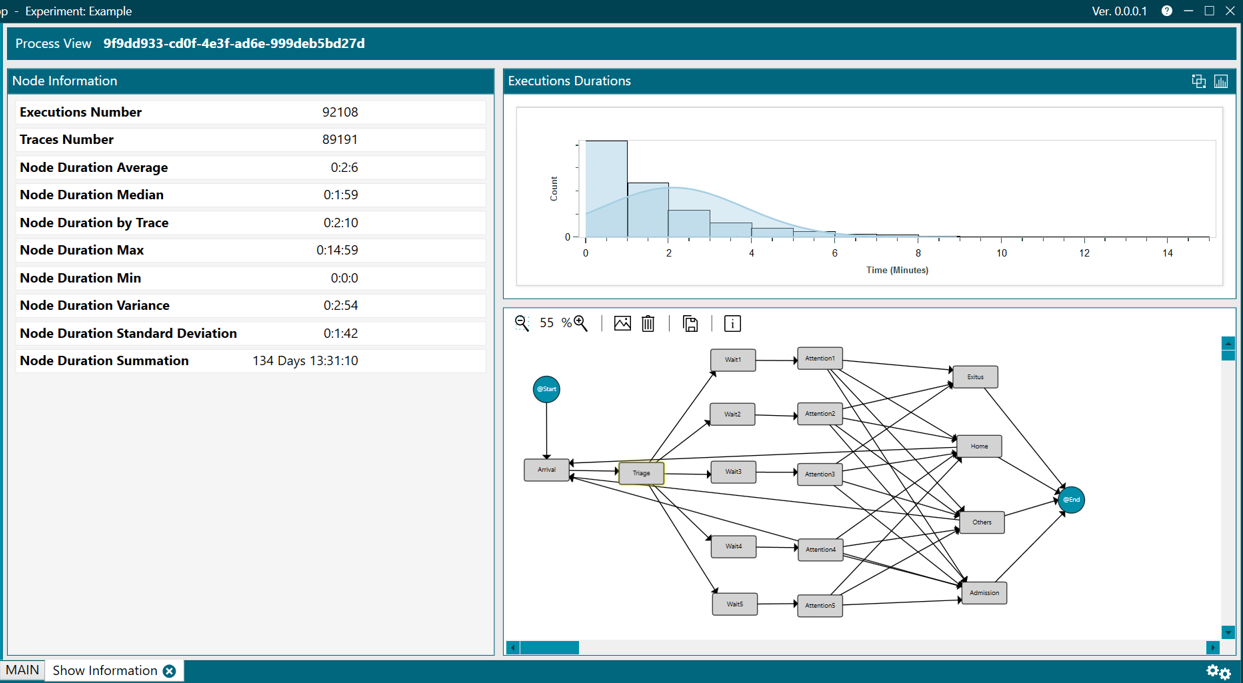
Figure 1. Node information
Statistics
The meaning of each statistic is the following:
- Executions Number. Number of executions in that node.
- Traces Number. Number of traces that traverse that node.
- Duration Average. Average duration of all executions of that node.
- Duration Median. Median of the duration of all executions of that node.
- Duration by Trace. Time of all the executions of that node divided by number of traces that traverse that node.
- Duration Max. Maximum duration among all executions of that node.
- Duration Min. Minimum duration among all executions of that node.
- Duration Variance. Variance of the duration of time of executions of that node.
- Duration Standard Deviation. Standard deviation of the duration of time of all executions of that node.
- Duration Summation. Summation of all times of all executions of that node.
Histogram
In the main header of the histogram, there are two options that allow:
-
Comparing process views (Compare process views) and
-
Calculating the Gaussian (Calculate gaussian mixture)
Compare process views
- When you click on option 1, a small text box appears (figure 2) where you have to select the process view against which you want to compare the current process.
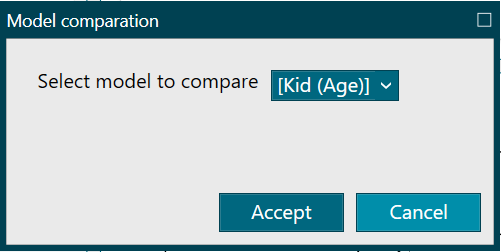
Figure 2. Compare process views
- A graph would be shown such as the one in figure 3, from where the histogram can be restored by clicking the Restore histogram button.
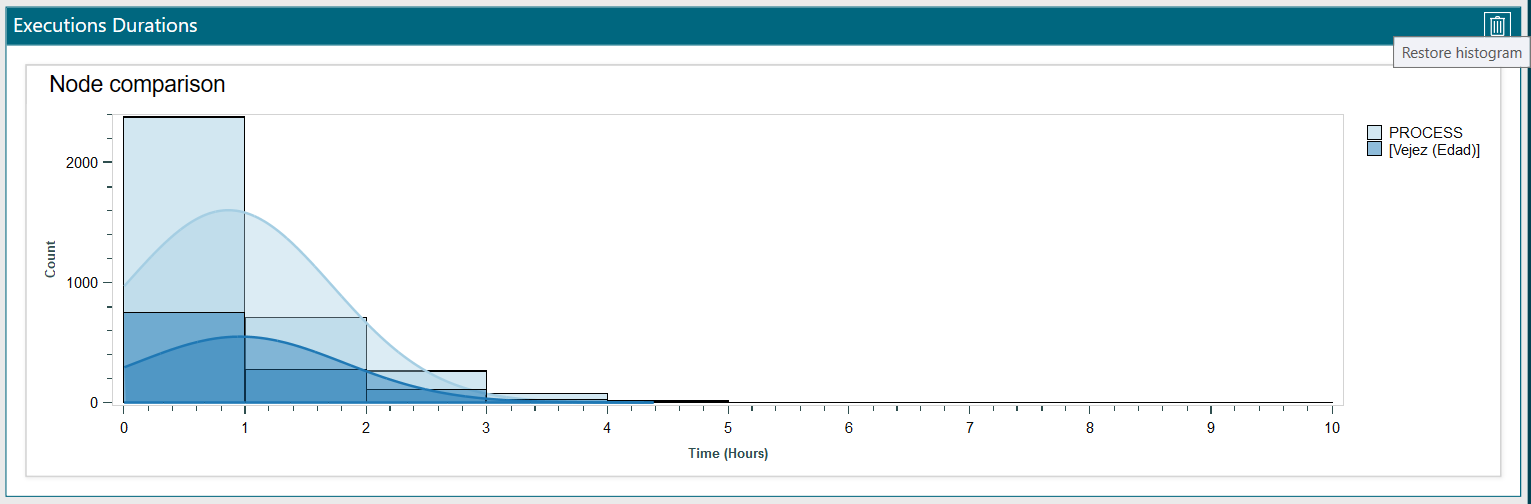
Figure 3. Comparison results
Calculate Gaussian mixture
- When you click on option 2, a small text box appears (figure 4) where you have to indicate how many gaussians you want to search
Figure 4. Calculate gaussian mixture
An example of the resulting graph is shown in figure 5, from where the following actions can be carried out:
-
Extract the data from the gaussians identified in a new experiment, where a new instance of the PMApp application would open,
-
Modify the number of Gaussians displayed,
-
Restore the histogram to its original state
In addition, as in the rest of the graphs in the application, if you hover the mouse over the header of the graph, a menu appears (as shown in figure 5).
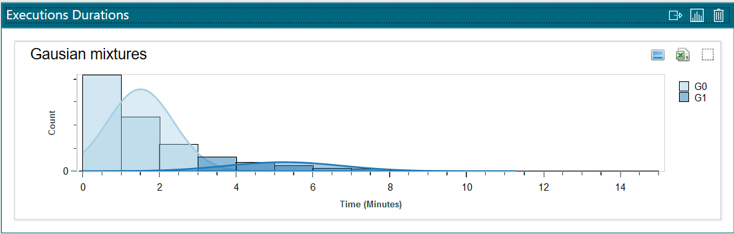
Figure 5. Charts menu
The available options are similar:
- Export as PNG
- Export the data to a CSV file
- Autoscale the chart to fit the available space
Finally, the represented histogram allows:
- Checking a specific value represented by the columns or Gaussian, by clicking with the left mouse button on the corresponding area,
- Scrolling the graph to the left or right by holding right click,
- With Ctrl + right click, it allows to select an area to zoom in, or you can also zoom in and out directly with Ctrl + mouse wheel. To restore the original size of the graph, as mentioned above, click on the Autoscale button available at the top right of the box for each graph.
This perspective has no main menu.